บทความวิชาการ
Oil Palm Tree Detection and Health Classification on High-Resolution Imagery Using Deep Learning
ชื่อวาระสาร: Agriculture (Scopus Indexed)
อันดับวารสาร: SCImago Journal Rank Quartile 2
Impact Factor: 2.072
1 Department of Geoinformatics, Rambhai Barni Rajabhat University, Chanthaburi 22000, Thailand
2Center for Spatial Information Science, The University of Tokyo, Chiba 277-8568, Japan
3 Department of Information and Communication Technologies, School of Engineering and Technology, Asian Institute of Technology, Pathumthani 12120, Thailand
4 Department of Geography, Faculty of Social Sciences, Srinakharinwirot University, Bangkok 10110, Thailand
Author to whom correspondence should be addressed.
Academic Editors: Sebastian Kujawa and Gniewko Niedbała
Agriculture 2021, 11(2), 183; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11020183
Received: 28 January 2021 / Revised: 16 February 2021 / Accepted: 20 February 2021 / Published: 23 February 2021
Abstract
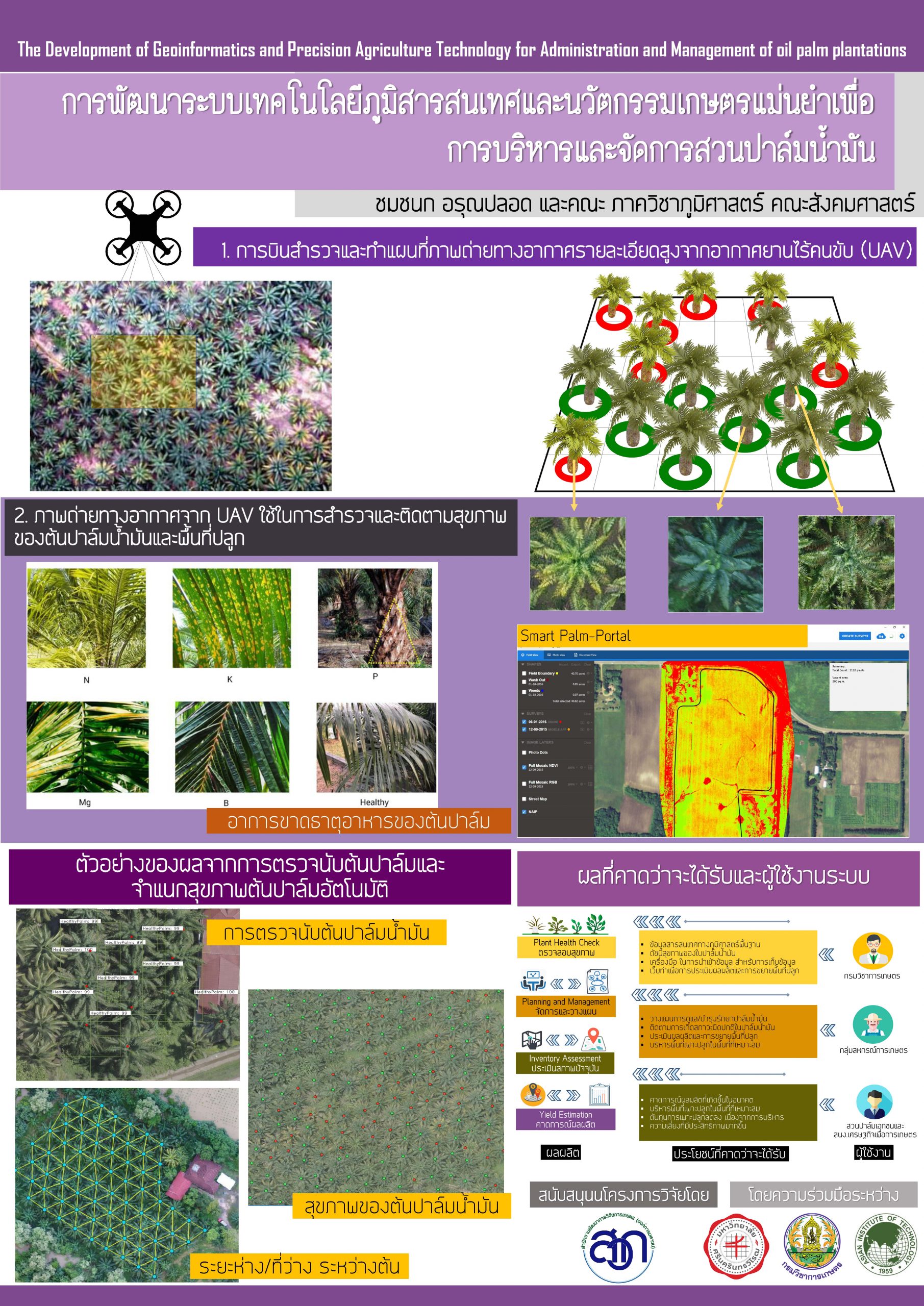
Combining modern technology and agriculture is an important consideration for the effective management of oil palm trees. In this study, an alternative method for oil palm tree management is proposed by applying high-resolution imagery, combined with Faster-RCNN, for automatic detection and health classification of oil palm trees. This study used a total of 4172 bounding boxes of healthy and unhealthy palm trees, constructed from 2000 pixel × 2000 pixel images. Of the total dataset, 90% was used for training and 10% was prepared for testing using Resnet-50 and VGG-16. Three techniques were used to assess the models’ performance: model training evaluation, evaluation using visual interpretation, and ground sampling inspections. The study identified three characteristics needed for detection and health classification: crown size, color, and density. The optimal altitude to capture images for detection and classification was determined to be 100 m, although the model showed satisfactory performance up to 140 m. For oil palm tree detection, healthy tree identification, and unhealthy tree identification, Resnet-50 obtained F1-scores of 95.09%, 92.07%, and 86.96%, respectively, with respect to visual interpretation ground truth and 97.67%, 95.30%, and 57.14%, respectively, with respect to ground sampling inspection ground truth. Resnet-50 yielded better F1-scores than VGG-16 in both evaluations. Therefore, the proposed method is well suited for the effective management of crops.
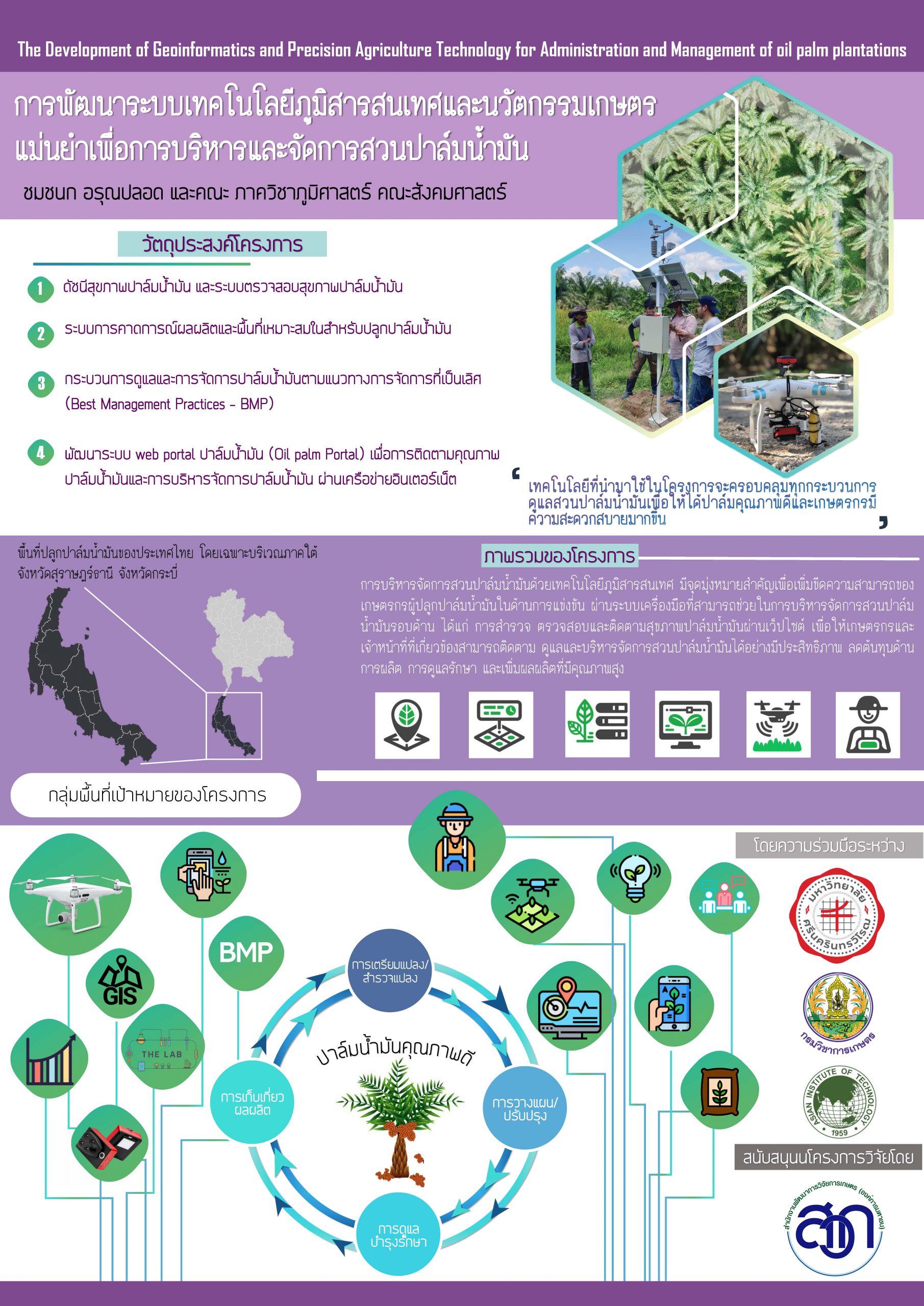
การพัฒนาระบบเทคโนโลยีภูมิสารสนเทศและนวัตกรรมเกษตรแม่นย้าเพื่อการบริหารและจัดการสวนปาล์มน้ำมัน
วันนิทรรศการวิชาการ รร.จปร.2562 วันที่ 19-20 พฤศจิกายน 2562
ณ โรงเรียนนายร้อยพระจุลจอมเกล้า
ณ โรงเรียนนายร้อยพระจุลจอมเกล้า